3.2 若干执行细节静态图的实际执行过程要比3.1节描述的复杂得多 。由于本篇的初衷不是做源码的完整剖析,因此我们仅就Client向Master的处理过程做详细说明,旨在让读者亲身体会一下交互过程的复杂性 。
Client创建GrpcSession,控制Client会话的生命周期;Master运行时被MasterSession控制 。GrpcSession通过抽象工厂模式得到,首先得到工厂类GrpcSessionFactory的对象,并用SessionFactory句柄factory存储 。然后通过factory的多态方法生成GrpcSession,如果target为grpc://的话 。Master本质上是一个Server,每个Server均有一个MasterService和一个WorkerService 。
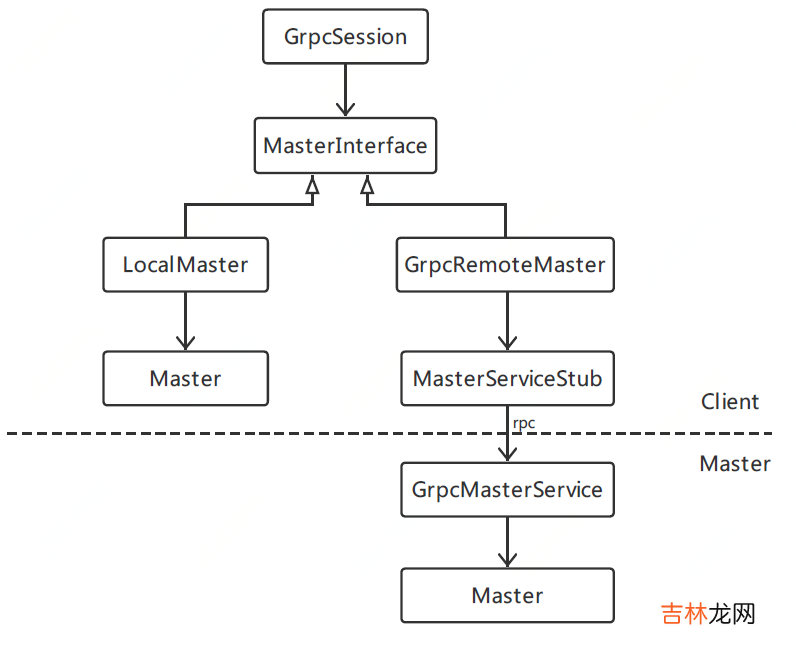
Client通过GrpcSession调用Master节点的MasterService,这个过程需借助MasterInterface才可完成 。MasterInterface用来和MasterService进行通信,它有两种不同的场景实现:
?如果Client和Master在同一个进程中,则用LocalMaster实现进程内的直接通信 。?GrpcRemoteMaster则使用gRPC来和MasterService进行通信,此时Master和Client在两个不同的进程中 。GrpcRemoteMaster的角色是gRPC客户端,它通过stub访问远程Master节点上的MasterService服务 。
文章插图
如果读者想对上述过程做更为深入的了解,可以参考几个关键类的源码:
?GrpcSession:core/distributed_runtime/rpc/grpc_session.h?LocalMaster:core/distributed_runtime/local_master.h?GrpcRemoteMaster:core/distributed_runtime/rpc/grpc_remote_master.cc?GrpcMasterService:core/distributed_runtime/rpc/grpc_master_service.cc其实Client到Master的处理过程还涉及MasterSession的创建,以及GrpcSession与MasterSession的交互与标识问题 。篇幅所限,不展开了 。
四、总结作为Dive into TensorFlow系列第一讲,本文由浅入深、系统讲解了静态图及其运行原理,以及支撑这些功能的架构设计与部分源码解析 。回到文章开头提到的用户读懂全文能有什么收益?(尝试提几点)
?明白默认session能运行默认静态图的原理,及常见的错误排查与调试方法 。能根据场景需要灵活选择动/静态图计算模式 。?如果一个静态图由几个独立子图构建,我们建议对每个子图分别构建tf.Graph对象 。?了解3.1小节对后续深入掌握op的placement、graph partition、基于gRPC的send/recv算子对做进程间通信有方向性指引作用 。作者:李杰参考资料1.Graphs and Sessions: https://github.com/tensorflow/docs/blob/master/site/en/r1/guide/graphs.md
2.《机器学习系统:设计与实现》: https://openmlsys.github.io/chapter_computational_graph/index.html
3.前后端连接的桥梁Session: https://www.likecs.com/show-306440850.html
4.TensorFlow v1.15.5源码: https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/tree/v1.15.5/tensorflow/core/graph
5.TensorFlow Architecture: https://github.com/tensorflow/docs/blob/master/site/en/r1/guide/extend/architecture.md
6.TensorFlow分布式环境Session: https://www.cnblogs.com/rossiXYZ/p/16065124.html
【1 Dive into TensorFlow系列-静态图运行原理】
经验总结扩展阅读
- TensorFlow?PyTorch?Paddle?AI工具库生态之争:ONNX将一统天下
- Tensorflow Lite从入门到精通
- WindivertDotnet快速发Ping
- 开源WindivertDotnet
- tensorflow-gpu版本安装及深度神经网络训练与cpu版本对比
- 附Anaconda安装包 Anaconda安装和卸载+虚拟环境Tensorflow安装以及末尾问题大全,这一篇就够了!!!
- 雅特TwinTop是什么
- into1刘宇个人简介 刘宇从艺历程
- 苹果笔记本历代型号
- 唇釉 13款宝藏国货唇釉口碑:INTO YOU素颜神器,橘朵色差较大












