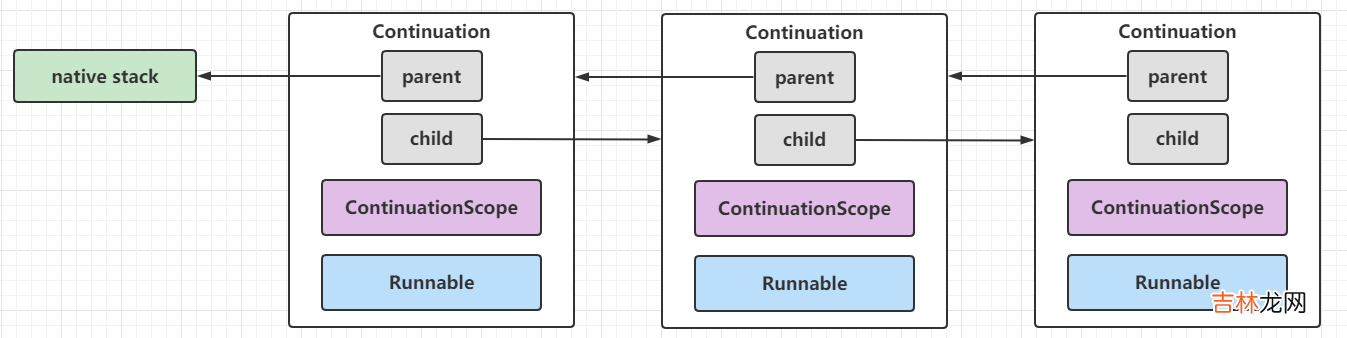
Continuation是一个双向链表设计,它的唯一一组构造参数是ContinuationScope和Runnable:
文章插图
这里不深入研究内部StackChunk、Pinned等实现,直接看run、enter系列方法和yield方法:
// Continuation.run()public final void run() { // 设置死循环 while (true) { // 进行mount操作 mount(); JLA.setExtentLocalCache(extentLocalCache); // 如果Continuation已完成则抛出异常 if (done) throw new IllegalStateException("Continuation terminated"); // 获取当前虚拟线程分配的运载线程 Thread t = currentCarrierThread(); if (parent != null) { if (parent != JLA.getContinuation(t)) throw new IllegalStateException(); } else this.parent = JLA.getContinuation(t); // 运载线程设置当前Continuation实例 JLA.setContinuation(t, this); try { // 判断ContinuationScope是否虚拟线程范围 boolean isVirtualThread = (scope == JLA.virtualThreadContinuationScope()); if (!isStarted()) { // is this the first run? (at this point we know !done) // 激活enter系列方法,标记isContinue为false,标记是否虚拟线程范围 enterSpecial(this, false, isVirtualThread); } else { assert !isEmpty(); // 激活enter系列方法,标记isContinue为true,标记是否虚拟线程范围 enterSpecial(this, true, isVirtualThread); } } finally { // 设置内存屏障 fence(); try { assert isEmpty() == done : "empty: " + isEmpty() + " done: " + done + " cont: " + Integer.toHexString(System.identityHashCode(this)); // 当前Continuation执行完成后,把运载线程的Continuation指向父Continuation JLA.setContinuation(currentCarrierThread(), this.parent); if (parent != null) parent.child = null; // 进行后置的yield清理工作 postYieldCleanup(); // 进行unmount操作 unmount(); // 判断是否需要保留当前线程的本地缓存并处理 if (PRESERVE_EXTENT_LOCAL_CACHE) { extentLocalCache = JLA.extentLocalCache(); } else { extentLocalCache = null; } JLA.setExtentLocalCache(null); } catch (Throwable e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.exit(1); } } // we're now in the parent continuation assert yieldInfo == null || yieldInfo instanceof ContinuationScope; // 父Continuation的yieldInfo缓存当前的scope实例,清空当前Continuation的父节点和yieldInfo if (yieldInfo == null || yieldInfo == scope) { this.parent = null; this.yieldInfo = null; // 这个位置是死循环的唯一跳出点 return; } else { // 执行到这个位置说明在当前是子Continuation并且进行了yield操作,需要跳转到父Continuation进行yield操作 parent.child = this; parent.yield0((ContinuationScope)yieldInfo, this); parent.child = null; } }}// Continuation.enter()系列方法// 这是一个native方法,它最终会根据判断回调到enter()方法private native static void enterSpecial(Continuation c, boolean isContinue, boolean isVirtualThread);// Continuation的入口方法,用户任务回调的入口@DontInline@IntrinsicCandidateprivate static void enter(Continuation c, boolean isContinue) { // This method runs in the "entry frame". // A yield jumps to this method's caller as if returning from this method. try { c.enter0(); } finally { c.finish(); }}// 真正任务包装器执行的回调方法private void enter0() { target.run();}// Continuation完成,标记done为trueprivate void finish() { done = true; assert isEmpty();}// Continuation.yield()方法,静态方法public static boolean yield(ContinuationScope scope) { // 获取当前运载线程的Continuation实例 Continuation cont = JLA.getContinuation(currentCarrierThread()); Continuation c; // 基于Continuation实例当前向父节点遍历,直到匹配虚拟线程类型的ContinuationScope的Continuation,如果没有匹配的Continuation会抛出异常中断流程 for (c = cont; c != null && c.scope != scope; c = c.parent) ; if (c == null) throw new IllegalStateException("Not in scope " + scope); // 把当前的Continuation挂起到给定的ContinuationScope return cont.yield0(scope, null);}// 透过上下文猜测是当前的Continuation实例挂起到给定的ContinuationScopeprivate boolean yield0(ContinuationScope scope, Continuation child) { // 强制抢占式卸载标记为false preempted = false; // 如果当前Continuation实例的yieldInfo不等于传入的ContinuationScope实例,则进行更新,相等的情况下yieldInfo会保持是一个空值 if (scope != this.scope) this.yieldInfo = scope; // 最终的yield调用,最终当前Continuation就是阻塞在此方法,从下文源码猜测,当该方法唤醒后,res值为0的时候,当前Continuation实例会继续执行,返回其他值的时候则会打印pined线程栈 int res = doYield(); // 放置内存屏障防止指令重排,后面注释提到是防止编译器进行某些转换 U.storeFence(); // needed to prevent certain transformations by the compiler assert scope != this.scope || yieldInfo == null : "scope: " + scope + " this.scope: " + this.scope + " yieldInfo: " + yieldInfo + " res: " + res; assert yieldInfo == null || scope == this.scope || yieldInfo instanceof Integer : "scope: " + scope + " this.scope: " + this.scope + " yieldInfo: " + yieldInfo + " res: " + res; if (child != null) { // TODO: ugly <----- 这个位置还有一句吐槽的代码注释:丑陋的代码 if (res != 0) { child.yieldInfo = res; } else if (yieldInfo != null) { assert yieldInfo instanceof Integer; child.yieldInfo = yieldInfo; } else { child.yieldInfo = res; } this.yieldInfo = null; } else { if (res == 0 && yieldInfo != null) { res = (Integer)yieldInfo; } this.yieldInfo = null; if (res == 0) // Continuation实例继续执行前回调 onContinue(); else // Continuation固定在运载线程前回调,res是pined的级别 onPinned0(res); } assert yieldInfo == null; // 返回布尔值结果表示当前Continuation实例是否会继续执行 return res == 0;}// 最终的yield调用,看实现是抛出异常,猜测是由JVM实现@IntrinsicCandidateprivate static int doYield() { throw new Error("Intrinsic not installed"); }
经验总结扩展阅读
- 第一篇 TTD 专题 :C# 那些短命线程都在干什么?
- Java并发编程 | 从进程、线程到并发问题实例解决
- 七 Netty 学习:NioEventLoop 对应线程的创建和启动源码说明
- 云原生虚拟网络 tun/tap & veth-pair
- 补充部分---ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor类分析 线程池底层原理详解与源码分析
- 附Anaconda安装包 Anaconda安装和卸载+虚拟环境Tensorflow安装以及末尾问题大全,这一篇就够了!!!
- 虚拟发货怎么确认收货
- 建议收藏 Java线程同步的四种方式详解
- 用AR Engine手部骨骼跟踪能力实现虚拟手表试戴
- 通过Thread Pool Executor类解析线程池执行任务的核心流程









