这里就是做了一些初始化工作,把需要的成员变量都解析出来,方便后面destroy时使用 。
然后我们看看destroy方法:
public void destroy() {// 调用所有DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor的postProcessBeforeDestructionif (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.beanPostProcessors)) {for (DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor processor : this.beanPostProcessors) {processor.postProcessBeforeDestruction(this.bean, this.beanName);}}// 如果是一个disposableBean,调用它的destroyif (this.invokeDisposableBean) {((DisposableBean) this.bean).destroy();}// 如果是AutoCloseable(并且自定义销毁方法名也是close),直接调用closeif (this.invokeAutoCloseable) {((AutoCloseable) this.bean).close();}// 否则去调用自定义方法else if (this.destroyMethod != null) {invokeCustomDestroyMethod(this.destroyMethod);}// 有可能存在destroyMethod没解析,但是destroyMethodName有了的情况,解析并调用else if (this.destroyMethodName != null) {Method destroyMethod = determineDestroyMethod(this.destroyMethodName);if (destroyMethod != null) {invokeCustomDestroyMethod(ClassUtils.getInterfaceMethodIfPossible(destroyMethod, this.bean.getClass()));}}}实战DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor#创建DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor
public class MyDestructionProcessor implements DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor {@Overridepublic void postProcessBeforeDestruction(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {System.out.println("[+] DestructionProcessor : " + beanName);}}向工厂中添加BeanPostProcessor,并销毁Bean:
factory.addBeanPostProcessor(new MyDestructionProcessor());factory.destroyBean("workbench", workbench);结果:
Workbench(operator=Person(name=Yudoge))[+] DestructionProcessor : top.yudoge.springserials.basic.beanfactory.beans.Workbench实战DisposableBean#让Bean实现DisposableBean
@Datapublic class Workbench implements DisposableBean {@Autowiredprivate Person operator;@Overridepublic void destroy() throws Exception {System.out.println("DisposableBean destroy");}}结果:
Workbench(operator=Person(name=Yudoge))[+] DestructionProcessor : top.yudoge.springserials.basic.beanfactory.beans.WorkbenchDisposableBean destroy实战CustomDestroyMethod#添加自定义销毁方法
@Datapublic class Workbench implements DisposableBean {@Autowiredprivate Person operator;@Overridepublic void destroy() throws Exception {System.out.println("DisposableBean destroy");}public void customDestroyMethod() {System.out.println("Custom destroy method...");}}在BeanDefinition中定义:
workbenchRbd.setDestroyMethodName("customDestroyMethod");结果:
Workbench(operator=Person(name=Yudoge))[+] DestructionProcessor : workbenchDisposableBean destroyCustom destroy method...总结#现在,Bean销毁阶段的逻辑已经全部理解完毕
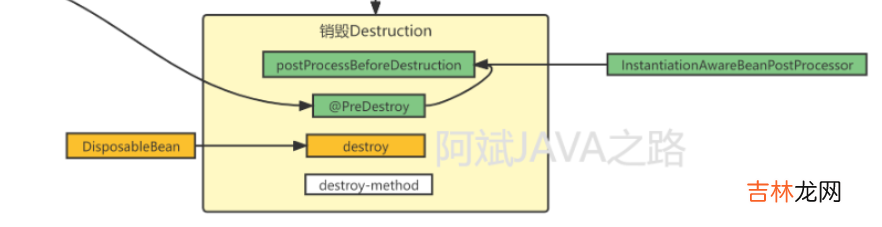
文章插图
- 调用DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor的before销毁方法
- 如果实现了DisposableBean,调用它的Destroy方法
- 调用自定义destroy-method方法
- 说明:真正意义上的销毁(从容器中移除bean)是在AbstractApplicationContext.close方法中实现的,在此方法中不仅会将bean从容器中移除,还会调用到我们实现的这些回调相关的方法 。
- 从BeanDefinition获取Bean信息
- 调用
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor的before实例化方法 - 如果它返回一个对象,那么直接进入该对象的初始化后方法
- 否则,它返回null,进入正常的Bean生命周期
- 实例化Bean
- 调用
populateBean,该方法的目的是对Bean属性进行设置 - 调用
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor经验总结扩展阅读
- 2023年农历八月初一砍树吉日 2023年9月15日砍树好吗
- 2023年9月15日买宠物好不好 2023年9月15日买宠物好吗
- 2023年9月15日是买狗的黄道吉日吗 2023年9月15日买狗黄道吉日
- 2023年9月15日买猫行吗 2023年9月15日是买猫吉日吗
- 2023年1月28日买牛好吗 2023年1月28日是买牛吉日吗
- 2023年农历八月初一买鸡吉日 2023年9月15日买鸡好不好
- 2023年9月15日是买鸭吉日吗 2023年农历八月初一买鸭吉日
- 2023年农历正月初七买猫吉日 2023年1月28日适合买猫吗
- 2023年农历正月初七宜砍树吗 2023年1月28日砍树吉日一览表
- 2023年1月28日适合塑绘吗 2023年1月28日塑绘黄道吉日












