所以,BeanFactory先是对于实现了InitializingBean的Bean的afterPropertiesSet进行调用,然后再对用户指定的init-method进行调用 。
InitializingBean实战#@Datapublic class Workbench implements InitializingBean {@Autowiredprivate Person operator;@Overridepublic void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {System.out.println("afterPropertiesSet");}}结果:
afterPropertiesSetWorkbench(operator=Person(name=Yudoge))init-method实战#添加init方法
@Datapublic class Workbench implements InitializingBean {@Autowiredprivate Person operator;@Overridepublic void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {System.out.println("afterPropertiesSet");}public void init() {System.out.println("init");}}向BeanDefinition中设置init方法名
// 设置Init方法名workbenchRbd.setInitMethodName("init");结果
afterPropertiesSetinitWorkbench(operator=Person(name=Yudoge))关于@PostConstruct#貌似BeanFactory并不支持@PostConstruct,它好像是ApplicationContext通过预注册InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor实现的 。这是我猜的 。
BeanPostProcessor.post初始化#略,因为前面已经讲了够多了,猜也能猜到怎么实现的
初始化阶段总结#
- 调用Aware方法
- 调用BeanPostProcessor的before初始化
- 如果是InitializingBean,调用afterPropertiesSet方法
- 如果有
init-method,调用 - 调用BeanPostProcessor的after初始化
文章插图
回到
doCreateBean方法中,最后,该方法判断了,如果必要的话就将该Bean注册到DisposableBean中:try {registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);}catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {}我猜其中的逻辑就是看看该Bean是不是DisposableBean的实例,如果是,注册到一个什么表中,方便销毁Bean时调用它的destory方法 。我们先不管,先看BeanFactory中有没有什么
destroyBean这种方法 。果然,在ConfigurableBeanFactory中定义了这个方法,AbstractBeanFactory把它实现了:@Overridepublic void destroyBean(String beanName, Object beanInstance) {destroyBean(beanName, beanInstance, getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName));}protected void destroyBean(String beanName, Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {new DisposableBeanAdapter(bean, beanName, mbd, getBeanPostProcessorCache().destructionAware, getAccessControlContext()).destroy();}这里创建了一个什么DisposableBeanAdapter,然后调用了destroy方法,就没干别的了 。DisposableBeanAdapter#
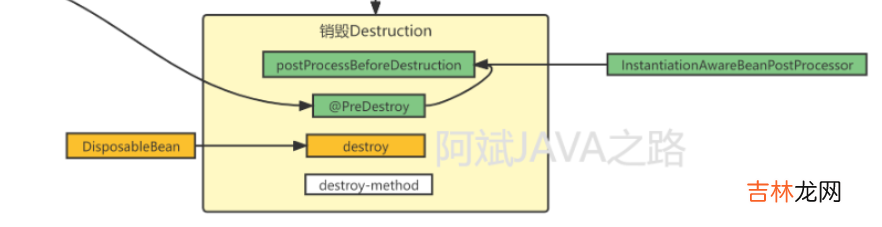
DisposableBeanAdapter的描述如下:/** * 实现了`DisposableBean`和`Runnable`的Adapter,对给定的Bean执行多个销毁步骤: * *- DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessors; *- 本身就实现了DisposableBean的Bean *- BeanDefinition中定义的Bean销毁方法 */class DisposableBeanAdapter implements DisposableBean, Runnable, Serializable所以,看起来,整个Bean的销毁步骤都是这哥们儿一个人完成的喽 。
文章插图
不过这个图应该画错了,它把
DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessors写成了InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 。看看它被调用的构造方法里写了啥:
public DisposableBeanAdapter(Object bean, String beanName, RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition,List<DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor> postProcessors, @Nullable AccessControlContext acc) {this.bean = bean;this.beanName = beanName;this.nonPublicAccessAllowed = beanDefinition.isNonPublicAccessAllowed();// 该Bean是不是可调用的DisposableBeanthis.invokeDisposableBean = (bean instanceof DisposableBean &&!beanDefinition.hasAnyExternallyManagedDestroyMethod(DESTROY_METHOD_NAME));// destroy方法名String destroyMethodName = inferDestroyMethodIfNecessary(bean, beanDefinition);// 和初始化哪里一样,防止destroy方法名和DisposableBean的方法名一样,重复调用if (destroyMethodName != null &&!(this.invokeDisposableBean && DESTROY_METHOD_NAME.equals(destroyMethodName)) &&!beanDefinition.hasAnyExternallyManagedDestroyMethod(destroyMethodName)) {// 如果Bean是一个AutoClosable并且自定义的销毁方法名也是close的话this.invokeAutoCloseable = (bean instanceof AutoCloseable && CLOSE_METHOD_NAME.equals(destroyMethodName));if (!this.invokeAutoCloseable) {// 如果不是,destroyMethodName就使用用户指定的并解析对应方法this.destroyMethodName = destroyMethodName;Method destroyMethod = determineDestroyMethod(destroyMethodName);// 省略一些destroy method参数设置相关的代码this.destroyMethod = destroyMethod;}}// 获取beanPostProcessors(filterPostProcessors会过滤掉所有非DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor的类)this.beanPostProcessors = filterPostProcessors(postProcessors, bean);this.acc = acc;}
经验总结扩展阅读
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- 2023年农历八月初一砍树吉日 2023年9月15日砍树好吗
- 2023年9月15日买宠物好不好 2023年9月15日买宠物好吗
- 2023年9月15日是买狗的黄道吉日吗 2023年9月15日买狗黄道吉日
- 2023年9月15日买猫行吗 2023年9月15日是买猫吉日吗
- 2023年1月28日买牛好吗 2023年1月28日是买牛吉日吗
- 2023年农历八月初一买鸡吉日 2023年9月15日买鸡好不好
- 2023年9月15日是买鸭吉日吗 2023年农历八月初一买鸭吉日
- 2023年农历正月初七买猫吉日 2023年1月28日适合买猫吗
- 2023年农历正月初七宜砍树吗 2023年1月28日砍树吉日一览表
- 2023年1月28日适合塑绘吗 2023年1月28日塑绘黄道吉日













