结果:

文章插图
5.归约(reduce)归约 , 也称缩减 , 顾名思义 , 是把一个流缩减成一个值 , 能实现对集合求和、求乘积和求最值操作 。
public static void main(String[] args) {List<Person> personList = new ArrayList<>();personList.add(new Person("张三", 1000, 20, "男", "北京"));personList.add(new Person("李四", 2000, 21, "男", "南京"));personList.add(new Person("王五", 3000, 20, "女", "合肥"));personList.add(new Person("赵六", 4000, 22, "男", "四川"));personList.add(new Person("孙七", 5000, 25, "女", "上海"));// 求所有员工的工资之和、最高工资// 求工资之和方法1:Optional<Integer> sumSalary = personList.stream().map(Person::getSalary).reduce(Integer::sum);// 求工资之和方法2:Integer sumSalary2 = personList.stream().reduce(0, (sum, p) -> sum += p.getSalary(), Integer::sum);// 求最高工资方法1:Integer maxSalary = personList.stream().reduce(0, (max, p) -> max > p.getSalary() ? max : p.getSalary(), Integer::max);// 求最高工资方法2:Integer maxSalary2 = personList.stream().reduce(0, (max, p) -> max > p.getSalary() ? max : p.getSalary(), (max1, max2) -> max1 > max2 ? max1 : max2);// 求最高工资方法3:Integer maxSalary3 = personList.stream().map(Person::getSalary).reduce(Integer::max).get();System.out.println("工资之和 , 方法1:" + sumSalary);System.out.println("工资之和 , 方法2:" + sumSalary2);System.out.println("最高工资 , 方法1:" + maxSalary);System.out.println("最高工资 , 方法2:" + maxSalary2);System.out.println("最高工资 , 方法3:" + maxSalary3);}结果:
文章插图
6.收集(collect)
collect , 收集 , 可以说是内容最繁多、功能最丰富的部分了 。从字面上去理解 , 就是把一个流收集起来 , 最终可以是收集成一个值也可以收集成一个新的集合 。collect主要依赖java.util.stream.Collectors类内置的静态方法 。6.1归集(toList/toSet/toMap)因为流不存储数据 , 那么在流中的数据完成处理后 , 需要将流中的数据重新归集到新的集合里 。toList、toSet和toMap比较常用 , 另外还有toCollection、toConcurrentMap等复杂一些的用法 。
下面用一个案例演示toList、toSet和toMap:
public static void main(String[] args) {List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1, 3, 4, 8, 6, 2, 20, 13);List<Integer> list1 = list.stream().filter(a -> a % 2 == 0).collect(Collectors.toList());Set<Integer> list2 = list.stream().filter(a -> a % 2 == 0).collect(Collectors.toSet());System.out.println("被2整除的list集合" + list1);System.out.println("被2整除的set集合" + list2);List<Person> personList = new ArrayList<>();personList.add(new Person("张三", 1000, 20, "男", "北京"));personList.add(new Person("李四", 2000, 21, "男", "南京"));personList.add(new Person("王五", 3000, 20, "女", "合肥"));personList.add(new Person("赵六", 4000, 22, "男", "四川"));personList.add(new Person("孙七", 5000, 25, "女", "上海"));// 工资大于3000元的员工Map<String, Integer> map = personList.stream().filter(person -> person.getSalary() > 3000).collect(Collectors.toMap(Person::getName, person -> person.getSalary()));System.out.println("工资大于3000元的员工:" + map);}结果: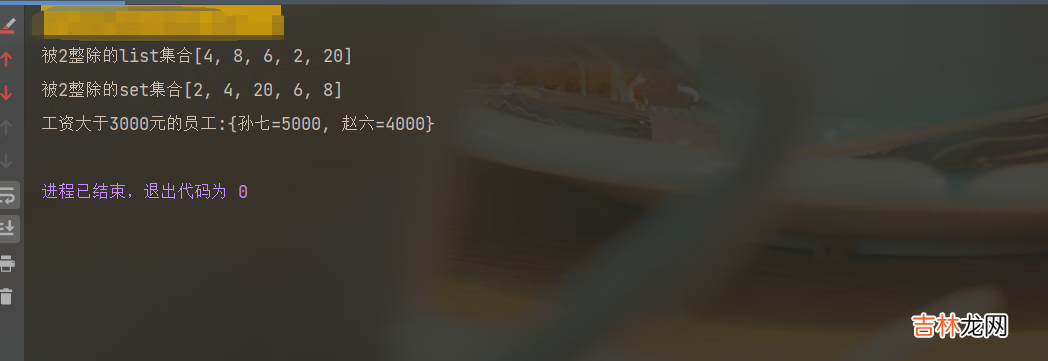
文章插图
6.2统计(count/averaging)Collectors提供了一系列用于数据统计的静态方法:
计数:count平均值:averagingInt、averagingLong、averagingDouble最值:maxBy、minBy求和:summingInt、summingLong、summingDouble统计以上所有:summarizingInt、summarizingLong、summarizingDouble
经验总结扩展阅读
- 苦瓜汤为什么要放黄豆
- 含熔喷布口罩能防病毒吗
- 22年平安夜是几月几日
- 苏打饼干含糖量高吗
- 奶茶店的果茶的危害
- 国旗护卫队138步和96步含义
- 立秋会凉快吗
- 达梦dba_segments指定表名查询到的大小都包含哪些数据
- Object Detection 【YOLOv5】LabVIEW+YOLOv5快速实现实时物体识别含源码
- 电蚊液有毒吗?需要开窗吗