public static void main(String[] args) {List<Person> personList = new ArrayList<>();personList.add(new Person("张三", 1000, 20, "男", "北京"));personList.add(new Person("李四", 2000, 21, "男", "南京"));personList.add(new Person("王五", 3000, 20, "女", "合肥"));personList.add(new Person("赵六", 4000, 22, "男", "四川"));personList.add(new Person("孙七", 5000, 25, "女", "上海"));// 筛选出工作高于3000的员工List<String> list = personList.stream().filter(p -> p.getSalary() > 3000).map(Person::getName).collect(Collectors.toList());System.out.println("薪资高于3000元的员工:" + list);}结果:
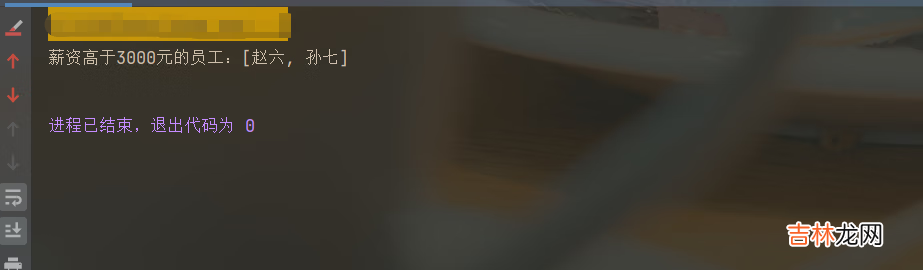
文章插图
3.聚合(max/min/count)
max、min、count这些大家都不陌生 , 在mysql中我们常用它们进行数据运算和统计 。Java stream中也引入了这些概念和用法 , 极大地方便了我们对集合、数组的数据统计工作 。public static void main(String[] args) {List<Person> personList = new ArrayList<>();personList.add(new Person("张三", 1000, 20, "男", "北京"));personList.add(new Person("李四", 2000, 21, "男", "南京"));personList.add(new Person("王五", 3000, 20, "女", "合肥"));personList.add(new Person("赵六", 4000, 22, "男", "四川"));personList.add(new Person("孙七", 5000, 25, "女", "上海"));// 获取工资最高的员工Optional<Person> max = personList.stream().max(Comparator.comparingInt(Person::getSalary));System.out.println("员工工资最大值:" + max.get().getSalary());// 计算工资大于2000的有多少人long count = personList.stream().filter(p -> p.getSalary() > 2000).count();System.out.println("工资大于2000元的人数:" + count);// 计算所有员工工资总和int sum = personList.stream().mapToInt(Person::getSalary).sum();System.out.println("所有员工工资总和:" + sum);}结果:
文章插图
4.映射(map/flatMap) 映射 , 可以将一个流的元素按照一定的映射规则映射到另一个流中 。分为
map和flatMap:map:接收一个函数作为参数 , 该函数会被应用到每个元素上 , 并将其映射成一个新的元素 。flatMap:接收一个函数作为参数 , 将流中的每个值都换成另一个流 , 然后把所有流连接成一个流 。
public static void main(String[] args) {List<Person> personList = new ArrayList<>();personList.add(new Person("张三", 1000, 20, "男", "北京"));personList.add(new Person("李四", 2000, 21, "男", "南京"));personList.add(new Person("王五", 3000, 20, "女", "合肥"));personList.add(new Person("赵六", 4000, 22, "男", "四川"));personList.add(new Person("孙七", 5000, 25, "女", "上海"));// 将员工工作全部增加10000元// 1、方式一:不改变原来员工集合List<Person> personListNew = personList.stream().map(person -> {Person personNew = new Person(person.getName(), 0, 0, null, null);personNew.setSalary(person.getSalary() + 10000);return personNew;}).collect(Collectors.toList());System.out.println("一次改动前:" + personList.get(0).getName() + ">>>" + personList.get(0).getSalary());System.out.println("一次改动后:" + personListNew.get(0).getName() + ">>>" + personListNew.get(0).getSalary());// 2、方式二:改变原来员工集合的方式List<Person> personListNew2 = personList.stream().map(person -> {person.setSalary(person.getSalary() + 10000);return person;}).collect(Collectors.toList());System.out.println("二次改动前:" + personList.get(0).getName() + ">>>" + personListNew.get(0).getSalary());System.out.println("二次改动后:" + personListNew2.get(0).getName() + ">>>" + personListNew.get(0).getSalary());// 将两个字符数组合并成一个新的字符数组List<String> list = Arrays.asList("Hello", "World");Stream<String> map = list.stream().map(s -> s.split("")).flatMap(Arrays::stream);map.forEach(System.out::print);System.out.println();// 给定两个数字列表 获取所有的数对List<Integer> numbers1 = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3);List<Integer> numbers2 = Arrays.asList(3, 4);// flatMap升维度List<int[]> pairs = numbers1.stream().flatMap(x -> numbers2.stream().map(y -> new int[] { x, y })).collect(Collectors.toList());for (int[] pair : pairs) {System.out.print(Arrays.toString(pair));}}
经验总结扩展阅读
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- 苦瓜汤为什么要放黄豆
- 含熔喷布口罩能防病毒吗
- 22年平安夜是几月几日
- 苏打饼干含糖量高吗
- 奶茶店的果茶的危害
- 国旗护卫队138步和96步含义
- 立秋会凉快吗
- 达梦dba_segments指定表名查询到的大小都包含哪些数据
- Object Detection 【YOLOv5】LabVIEW+YOLOv5快速实现实时物体识别含源码
- 电蚊液有毒吗?需要开窗吗