GGD 论文解读《Rethinking and Scaling Up Graph Contrastive Learning: An Extremely Efficient Approach with Group Discrimination》( 二 )
Bilinear :
$\mathcal{D}\left(\mathbf{h}_{i}, \mathbf{s}\right)=\sigma_{s i g}\left(\mathbf{h}_{i} \cdot \mathbf{W} \cdot \mathbf{s}\right)\quad\quad\quad(2)$
实验:替换 $\text{Eq.1}$ 中的 aggregation function ,即 sum 函数
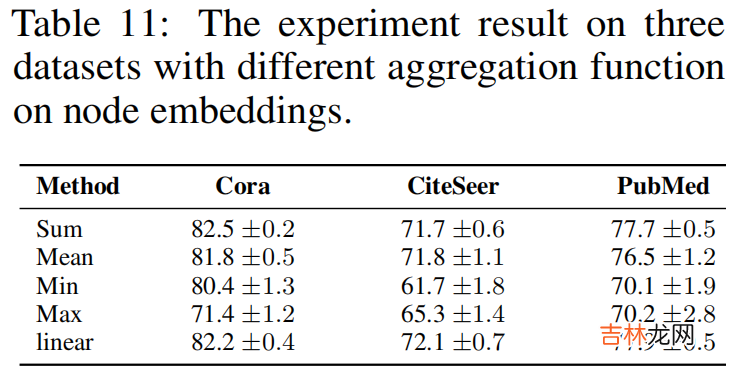
文章插图
替换形式为:
$\mathcal{L}_{B C E}=-\frac{1}{2 N}\left(\sum\limits _{i=1}^{2 N} y_{i} \log \hat{y}_{i}+\left(1-y_{i}\right) \log \left(1-\hat{y}_{i}\right)\right)\quad\quad\quad(3)$
其中,$\hat{y}_{i}=\operatorname{agg}\left(\mathbf{h}_{i}\right)$ ,$y_{i} \in \mathbb{R}^{1 \times 1}$ ,$\hat{y}_{i} \in \mathbb{R}^{1 \times 1}$ 。论文中阐述 $y_{i}$ 和 $\hat{y}_{i}$ 分别代表 node $i$ 是否是 postive sample ,及其预测输出 。Q :当 aggregation function 采用 $\text{mean}$ 的时候,对于 postive sample $i$ ,$\hat{y}_{i}$ 值会趋于 $1$ 么?
DGI 真正所做的是区分正确拓扑生成的一组节点和损坏拓扑生成的节点,如 Figure 1 所示 。可以这么理解,DGI 是使用一个固定的向量 $s$ 去区分两组节点嵌入矩阵(postive and negative) 。
为解决上述 GD 的问题,本文将考虑使用 $\text{Eq.3}$ 去替换 DGI 中的损失函数 。替换的好处:节省显存和加快计算速度,对于精度没啥改变,说的天花乱坠 。
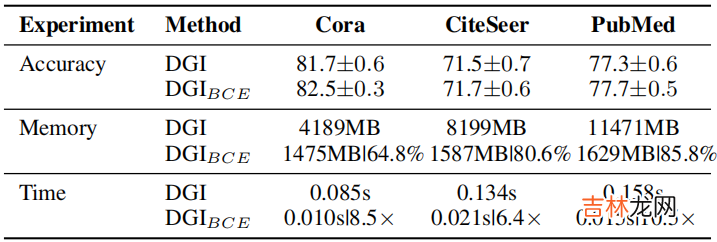
文章插图
Note:方差大的稍微大一点的 method ,就是容易被诋毁 。
Group Discrimination 定义:GRL method,将不同组别的节点划分给不同的组,对于 postive pair 和 negative pair 分别划分到 "1" 组 和 "0" 组 。3 Methodology整体框架:

文章插图
组成部分:
- Siamese Network :模仿 MVGRL 的架构;
- Data Augmentation :提供相似意义信息,带来的是时间成本;【dropout edge、feature mask】
- Loss function : $\text{Eq.3}$;
其次:MVGRL 多视图对比工作给本文深刻的启发,所以考虑引入全局信息 :$ \mathbf{H}_{\theta}^{\text {global }}=\mathbf{A}^{n} \mathbf{H}_{\theta}$;
最后:得到局部表示和全局表示的聚合 $\mathbf{H}=\mathbf{H}_{\theta}^{\text {global }}+\mathbf{H}_{\theta}$ ;
4 Experiments4.1 Datasets
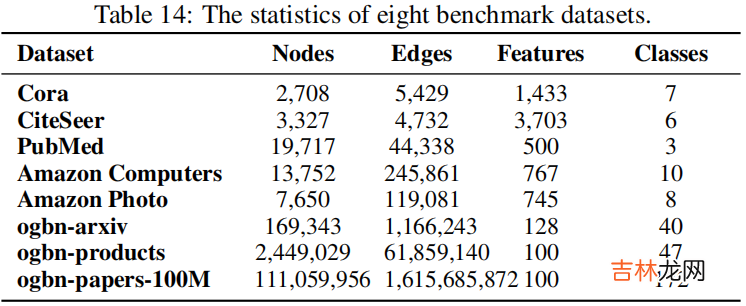
文章插图
4.2 Result节点分类
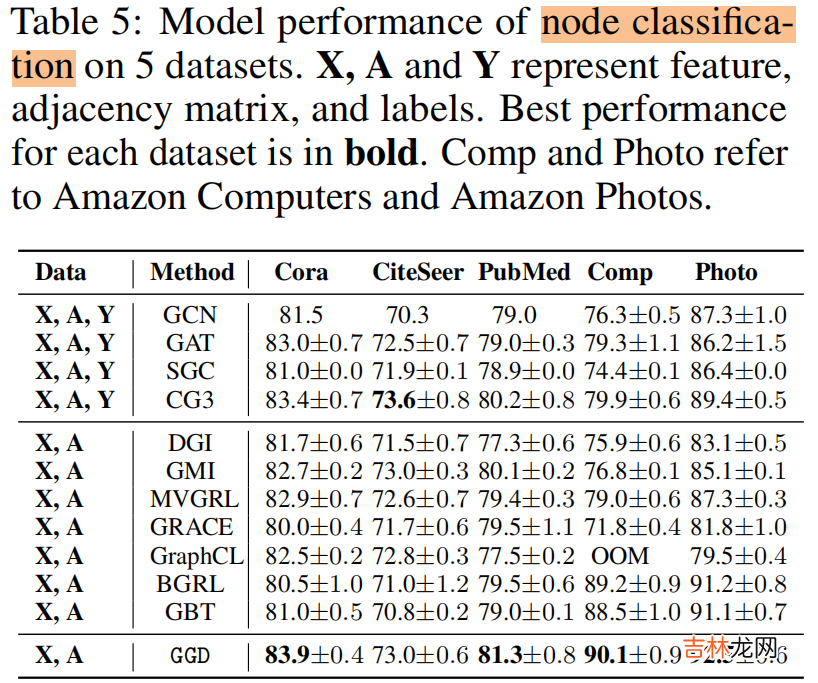
文章插图
训练时间 和 内存消耗
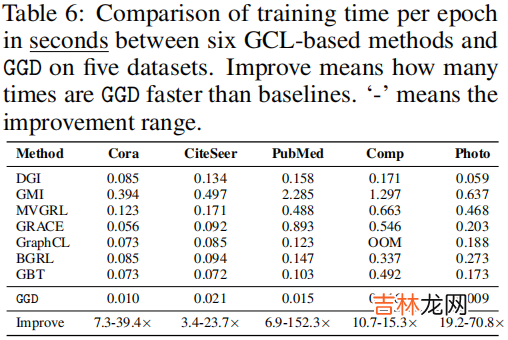
文章插图
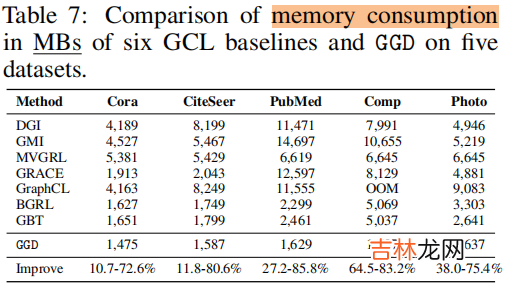
文章插图
4.3 Evaluating on Large-scale datasets

文章插图
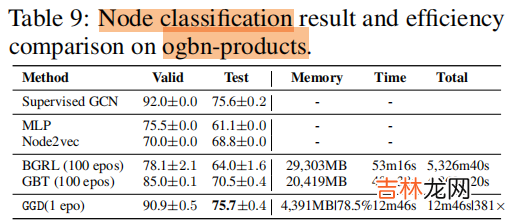
文章插图
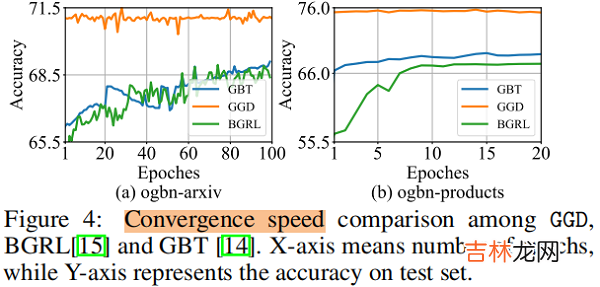
文章插图
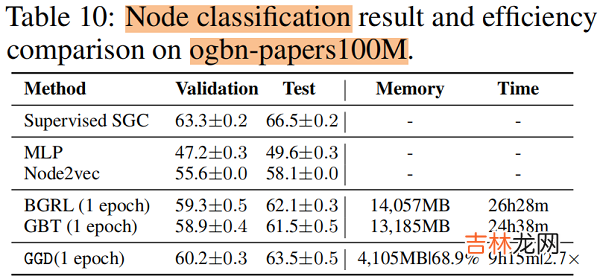
文章插图
5 Future Work For example, can we extend the current binary Group Discrimination scheme (i.e., classifying nodes generated with different topology) to discrimination among multiple groups?
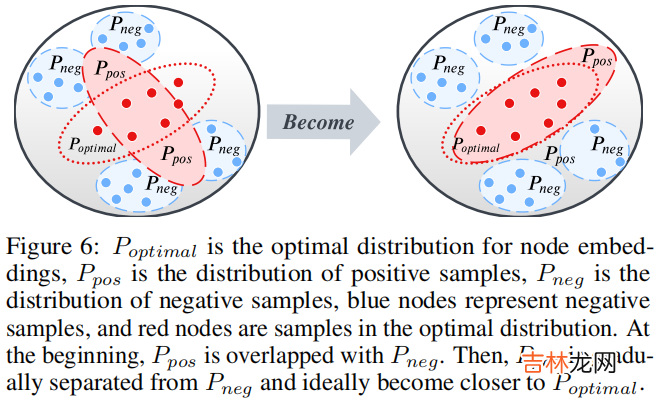
文章插图
经验总结扩展阅读
- ULID规范解读与实现原理
- 钩子 【pytest官方文档】解读-插件开发之hooks 函数
- AlexNet-文献阅读笔记
- 带你读AI论文丨ACGAN-动漫头像生成
- 深渊游戏结局解读
- 英语论文答辩技巧
- 如何解读芥川龙之介的秋山图
- 【论文翻译】KLMo: Knowledge Graph Enhanced Pretrained Language Model with Fine-Grained Relationships
- 大学生论文素材哪里找
- 毕业论文初稿怎么写