- The abbreviation “AT” in AT engine stands for air turbo.
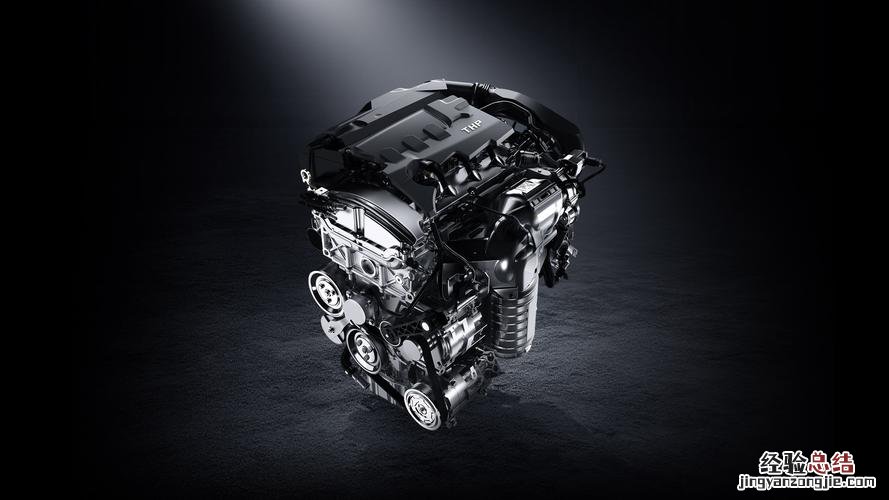
- AT engine refers to a type of internal combustion engine that utilizes turbocharging technology.
- Turbocharging is the process of using a turbine to compress the air entering the engine, resulting in increased power and efficiency.
- AT engines are commonly used in automobiles and aircraft, where the demand for high power output is essential.
- The turbocharger in an AT engine consists of a turbine and a compressor, which are connected by a shaft.
- As the exhaust gases pass through the turbine, it spins rapidly, driving the compressor to compress the incoming air.
- This compressed air is then fed into the engine’s combustion chamber, allowing for more efficient combustion and increased power.
- AT engines are particularly beneficial at high altitudes, where the air density is lower.
- The turbocharging technology compensates for the reduced air density, ensuring optimal performance at various altitudes.
- In summary, an AT engine refers to an internal combustion engine that utilizes turbocharging technology to enhance power and efficiency.