SpringBoot基础配置我们在Spring中能够实现的技术,在SpringBoot中同样可以实现
接下来我们依次来介绍一些SpringBoot基本配置的方法和多环境开发的问题
SpringBoot配置格式SpringBoot为我们提供了三种配置格式来管理SpringBoot的配置(注意:以下配置均存在于resources文件夹中):
- application.properties
# 修改服务器端口号为80server.port=80- application.yml (主流)
# 修改服务器端口号为81(注意:存在空格)server: port: 81- application.yaml
# 修改服务器端口号为82(注意:存在空格)server: port: 82当三者均存在时,其优先级为:application.properties>application.yml >application.yaml以上三种配置格式均在resources文件夹下创建相对应名称以及后缀的文件下书写:
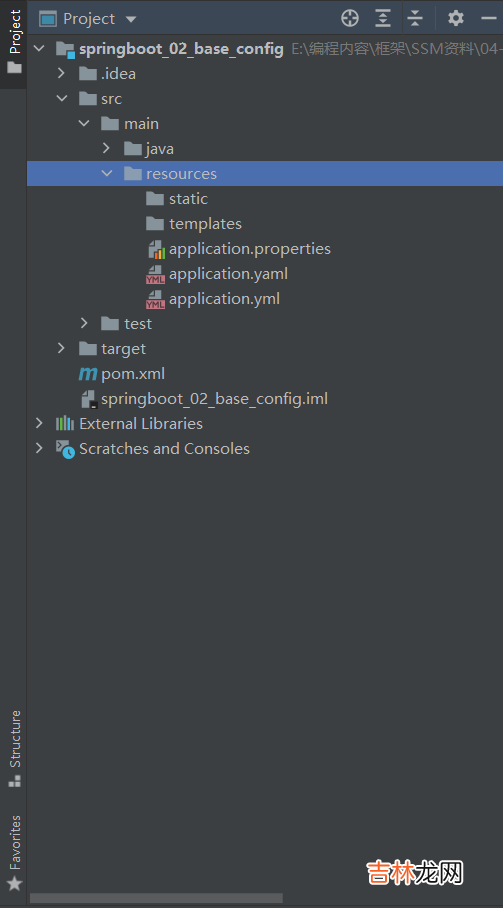
文章插图
注意:yaml文件详细介绍我们在这里详细介绍一下yaml文件:
application.properties属于SpringBoot自带,不需要创建
application.yml,application.yaml需要自我创建,因而不被标记为配置文件
如果我们希望该文件被标记为配置文件并包含有补全功能,我们需要手动设置为配置文件
- YAML,一种数据序列化格式
- 容易阅读
- 容易与脚本语言交互
- 以数据为核心,重数据轻格式
- .yml(主流)
- .yaml
- 大小写敏感
- 属性层级关系
- 使用缩进表示层级关系,同层级左侧对齐,只允许使用空格(不能使用tab)
- 属性值前面添加空格(属性名与属性值之间使用冒号+空格作为分隔)
- # 表示注释
- 使用 - 来表示数据开始符号(数组)
server:port: 82logging:level:root: infolikes:- music- game- PEYAML的数据读取方法:首先我们先给出我们在yml文件中所列出的属性:
lesson: SpringBootserver:port: 80enterprise:name: itcastage: 16tel: 4006184000subject:- Java- 前端- 大数据下面我们来介绍yaml数据读取的三种方法:- ${属性名},${属性名.属性名},${属性名.属性名[数组下标]}
package com.itheima.controller;import com.itheima.domain.Enterprise;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;@RestController@RequestMapping("/books")public class BookController {//使用@Value读取单一属性数据@Value("${lesson}")private String lesson;@Value("${server.port}")private Integer port;@Value("${enterprise.subject[0]}")private String subject_00;@GetMapping("/{id}")public String getById(@PathVariable Integer id){System.out.println(lesson);System.out.println(port);System.out.println(subject_00);return "hello , spring boot!";}}- Environment对象匹配方法
package com.itheima.controller;import com.itheima.domain.Enterprise;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;@RestController@RequestMapping("/books")public class BookController {//使用Environment封装全配置数据(自动装配封装Environment,里面会包含yaml中所有属性和属性值)@Autowiredprivate Environment environment;@GetMapping("/{id}")public String getById(@PathVariable Integer id){// 我们采用environment的getProperty方法,根据属性名,获得属性值System.out.println(environment.getProperty("lesson"));System.out.println(environment.getProperty("server.port"));System.out.println(environment.getProperty("enterprise.age"));System.out.println(environment.getProperty("enterprise.subject[1]"));return "hello , spring boot!";}}
经验总结扩展阅读
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- 法伯丽护肤品是哪里的护肤品品牌?
- 阿玛尼红气垫适合什么肤质?
- 阿玛尼满天星男生可以带吗?
- 阿玛尼满天星有几个版本?
- 阿玛尼护肤品适合年龄?
- 电视剧伪钞者之末路剧情介绍?
- 法兰琳卡什么档次的护肤品?
- 羽田浩司出现在哪一集?
- 电视剧羽你同行演员表介绍?
- 电视剧伪钞者之末路结局是什么?