Loss分类采用dice_loss,回归采用smooth_l1_loss 。
class EASTLoss(nn.Layer):def __init__(self,eps=1e-6,**kwargs):super(EASTLoss, self).__init__()self.dice_loss = DiceLoss(eps=eps)def forward(self, predicts, labels):"""Params:predicts: {'f_score': 前景得分图,'f_geo': 回归图}labels: [imgs, l_score, l_geo, l_mask]"""l_score, l_geo, l_mask = labels[1:]f_score = predicts['f_score']f_geo = predicts['f_geo']# 分类lossdice_loss = self.dice_loss(f_score, l_score, l_mask)channels = 8# channels+1的原因是最后一个图对应了短边的归一化系数(后面会讲),前8个代表相对偏移的label# [[b,1,h/4,w/4], ...]共9个l_geo_split = paddle.split(l_geo, num_or_sections=channels + 1, axis=1)# [[b,1,h/4,w/4], ...]共8个f_geo_split = paddle.split(f_geo, num_or_sections=channels, axis=1)smooth_l1 = 0for i in range(0, channels):geo_diff = l_geo_split[i] - f_geo_split[i]# diff=label-predabs_geo_diff = paddle.abs(geo_diff)# abs_diff# 计算abs_diff中小于1的且有文本的部分smooth_l1_sign = paddle.less_than(abs_geo_diff, l_score)smooth_l1_sign = paddle.cast(smooth_l1_sign, dtype='float32')# smoothl1 loss,大于1和小于1的两个部分对应loss相加,只不过这里<1的部分没乘0.5,问题不大in_loss = abs_geo_diff * abs_geo_diff * smooth_l1_sign + \(abs_geo_diff - 0.5) * (1.0 - smooth_l1_sign)# 用短边*8做归一化out_loss = l_geo_split[-1] / channels * in_loss * l_scoresmooth_l1 += out_loss# paddle.mean(smooth_l1)就可以了,前面都乘过了l_score,这里再乘没卵用smooth_l1_loss = paddle.mean(smooth_l1 * l_score)# dice_loss权重为0.01,smooth_l1_loss权重为1dice_loss = dice_loss * 0.01total_loss = dice_loss + smooth_l1_losslosses = {"loss":total_loss, \"dice_loss":dice_loss,\"smooth_l1_loss":smooth_l1_loss}return lossesDice Loss公式:
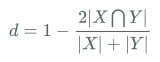
文章插图
代码:
class DiceLoss(nn.Layer):def __init__(self, eps=1e-6):super(DiceLoss, self).__init__()self.eps = epsdef forward(self, pred, gt, mask, weights=None):# mask代表了有效文本的mask,有文本的地方是1,否则为0assert pred.shape == gt.shapeassert pred.shape == mask.shapeif weights is not None:assert weights.shape == mask.shapemask = weights * maskintersection = paddle.sum(pred * gt * mask)# 交集union = paddle.sum(pred * mask) + paddle.sum(gt * mask) + self.eps# 并集loss = 1 - 2.0 * intersection / unionassert loss <= 1return lossSmoothL1 Loss公式:
文章插图
InferPostProcess
class EASTPostProcess(object):def __init__(self,score_thresh=0.8,cover_thresh=0.1,nms_thresh=0.2,**kwargs):self.score_thresh = score_threshself.cover_thresh = cover_threshself.nms_thresh = nms_thresh...def __call__(self, outs_dict, shape_list):score_list = outs_dict['f_score']# shape=[b,1,h//4,w//4]geo_list = outs_dict['f_geo']# shape=[b,8,h//4,w//4]if isinstance(score_list, paddle.Tensor):score_list = score_list.numpy()geo_list = geo_list.numpy()img_num = len(shape_list)dt_boxes_list = []for ino in range(img_num):score = score_list[ino]geo = geo_list[ino]# 根据score、geo以及一些预设阈值和locality_nms操作拿到检测框boxes = self.detect(score_map=score,geo_map=geo,score_thresh=self.score_thresh,cover_thresh=self.cover_thresh,nms_thresh=self.nms_thresh)boxes_norm = []if len(boxes) > 0:h, w = score.shape[1:]src_h, src_w, ratio_h, ratio_w = shape_list[ino]boxes = boxes[:, :8].reshape((-1, 4, 2))# 文本框坐标根于缩放系数映射回输入图像上boxes[:, :, 0] /= ratio_wboxes[:, :, 1] /= ratio_hfor i_box, box in enumerate(boxes):# 根据宽度比高度大这一先验,将坐标调整为以“左上角”点为起始点的顺时针4点框box = self.sort_poly(box.astype(np.int32))# 边长小于5的再进行一次过滤,拿到最终的检测结果if np.linalg.norm(box[0] - box[1]) < 5 \or np.linalg.norm(box[3] - box[0]) < 5:continueboxes_norm.append(box)dt_boxes_list.append({'points': np.array(boxes_norm)})return dt_boxes_listdef detect(self,score_map,geo_map,score_thresh=0.8,cover_thresh=0.1,nms_thresh=0.2):score_map = score_map[0] # shape=[h//4,w//4]geo_map = np.swapaxes(geo_map, 1, 0)geo_map = np.swapaxes(geo_map, 1, 2)# shape=[h//4,w//4,8]# 获取score_map上得分大于阈值的点的坐标,shape=[n,2]xy_text = np.argwhere(score_map > score_thresh)if len(xy_text) == 0:return []# 按y轴从小到大的顺序对这些点进行排序xy_text = xy_text[np.argsort(xy_text[:, 0])]# 恢复成基于原图的文本框坐标text_box_restored = self.restore_rectangle_quad(xy_text[:, ::-1] * 4, geo_map[xy_text[:, 0], xy_text[:, 1], :])# shape=[n,9] 前8个通道代表x1,y1,x2,y2的坐标,最后一个通道代表每个框的得分boxes = np.zeros((text_box_restored.shape[0], 9), dtype=np.float32)boxes[:, :8] = text_box_restored.reshape((-1, 8))boxes[:, 8] = score_map[xy_text[:, 0], xy_text[:, 1]]try:import lanmsboxes = lanms.merge_quadrangle_n9(boxes, nms_thresh)except:print('you should install lanms by pip3 install lanms-nova to speed up nms_locality')# locality nms,比传统nms要快,因为进入nms中的文本框的数量要比之前少很多 。前面按y轴排序其实是在为该步骤做铺垫boxes = nms_locality(boxes.astype(np.float64), nms_thresh)if boxes.shape[0] == 0:return []# 最终还会根据框预测出的文本框内的像素在score_map上的得分再做一次过滤,感觉有一些不合理,因为score_map# 上预测的是shrink_mask,会导致框内有很多背景像素,拉低平均得分,可能会让一些原本有效的文本框变得无效# 当然这里的cover_thresh取的比较低,可能影响就比较小for i, box in enumerate(boxes):mask = np.zeros_like(score_map, dtype=np.uint8)cv2.fillPoly(mask, box[:8].reshape((-1, 4, 2)).astype(np.int32) // 4, 1)boxes[i, 8] = cv2.mean(score_map, mask)[0]boxes = boxes[boxes[:, 8] > cover_thresh]return boxesdef nms_locality(polys, thres=0.3):def weighted_merge(g, p):"""框间merge的逻辑:坐标变为coor1*score1+coor2*score2,得分变为score1+score2"""g[:8] = (g[8] * g[:8] + p[8] * p[:8]) / (g[8] + p[8])g[8] = (g[8] + p[8])return gS = []p = Nonefor g in polys:# 由于是按y轴排了序,所以循环遍历就可以了if p is not None and intersection(g, p) > thres:# 交集大于阈值那么就mergep = weighted_merge(g, p)else:# 不能再merge的时候该框临近区域已无其他框,那么其加入进Sif p is not None:S.append(p)p = gif p is not None:S.append(p)if len(S) == 0:return np.array([])# 将S保留下的文本框进行标准nms,略return standard_nms(np.array(S), thres)
经验总结扩展阅读
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Linux 文件操作接口
- 『现学现忘』Git分支 — 38、Git分支介绍
- ciscn 2022 misc 部分wp
- 强国杯东杯分区赛miscwp
- aws上传文件、删除文件、图像识别
- 【linux】 第1回 linux运维基础
- JSP页面实现验证码校验
- gradle项目对比maven项目的目录架构以及对gradle wrapper的理解
- BigDecimal 用法总结
- mac通过docker一键部署Nexus3












